Today the following note will be entirely devoted to a very entertaining and promising technology (so to speak, ” the “golden vein” of the IT industry), hiding under a pseudonym – cloud technologies or in the common people – “cloud.”
We will talk about the concept of cloud computing, give a variety of examples of its implementation (at the level of solutions for ordinary users). Namely, we will talk about the theory, then smoothly move on to practice and a little. in the clouds:-)

Thus, our note’s purpose, as always good (in another way and can not be) – to organize the basic information related to this topic and put everything on the shelves.
So, Earthlings, get ready; now we’re going to talk about cloud technologies that are getting closer and closer to us every day.
- About everything, little by little
- More details about cloud technology
- Cloud services
- Cloud Computing Opportunities
- Cloud technology is a user’s view. Solution review
- Dealing with documents in cloud technology
- Cloud technology and data storage
About everything, little by little
In recent years, this topic has become one of the most popular in the IT-sphere, it is written a lot of articles, held even more conferences, and how many solutions already exist on the market (and in all used by us in everyday life, sometimes even unconsciously), and do not count at all.
However, as always, there is one “but”namely, most users still do not know what kind of “know-how” cloud technology and for what it generally gave up. We will correct the situation and start, as it should, with the theory.
Cloud computing is a distributed data processing technology in which computer resources and power are provided to the user as an Internet service. If you explain the accessible language, it is your, in a sense, a work platform on the Internet, or rather on a remote server.
Let’s look at the example to make sure that almost every one of us, one way or another, has already encountered a sim solution.
Do you have an e-mail? Of course, I do. If you work with mail on some site-service (for example, Gmail), which this mail allows you to use, this is nothing but a cloud service, which is part of such a thing as cloud technology. Or, for example, image processing.
If you reduce the size, turn your photo in Photoshop or another particular program, you have nothing to do with cloud technology. Everything happens and is processed locally on your computer. But if having downloaded the image, for example, through the service Picasa, you process it on the other side, to be in the browser, then this is the “cloud.”
More details about cloud technology
The difference lies solely in the method of storing and processing data. If all the operations take place on your computer (using its capabilities), it is not a “cloud,” and if the process takes place on the server in the network, it is precisely the trend thing, which is called “cloud technology.”
In other words, cloud technologies are various hardware, software, methodologies, and tools provided to the user, like Internet services, to realize their goals, objectives, and projects.
As practice shows, the terms “cloud technologies”/”cloud service,” with their generally accepted graphic representation, in the form of “clouds,” only confuses users; their structure can be easily understood if you imagine it as the next pyramid.
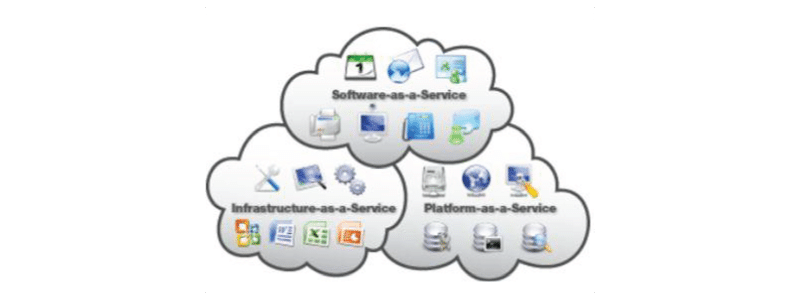
The base of the pyramid “infrastructure” is a set of physical devices (servers, hard drives, etc.); above it is built “platform” – a set of services and the top – software available at the request of users.
Also, it should be known that cloud computing is a base vector derived from the synthesis of several technologies and approaches.
I think that now it has become a little clearer, the benefit of the scheme is quite simple. However, in general terms, cloud technology is such a kind of porridge, which performs calculations by servers and other things without directly attracting your computer’s resources.
It may turn out that we will all return to computers that are close to, so to speak, the first and will be only a screen with a microprocessor, and all calculations and power will be located and produced remotely, i.e., in somewhere living servers, namely, in the mentioned repeatedly Cloud.
Cloud Services
Currently, cloud technologies, and their concept, involves providing the following types of services to their users:
- Storage-as-a-Service (“storage as a service”) is perhaps the easiest of services, disk space on demand. Each of us has ever encountered a situation where an ominous warning appeared on the monitor: “The logical disk is filled to make room, delete unnecessary programs or data.” Storage-as-a-Service allows you to store data in external storage in the Cloud. For you, it will look like an extra logical drive or folder. The service is essential for the rest, as it is part of almost every one of them. An example is Google Drive and other similar services.
- Database-as-a-Service (“database as a service”) Here is somewhat more for admins because it provides an opportunity to work with databases as if the database was installed on a local resource. Moreover, in this case, it is much easier to “spread” projects between different executors, not to mention how much money can be saved on the computer iron and licenses required for the clever use of the database in a large or even medium-sized organization.
- Information-as-a-Service (“information as a service”) allows you to remotely use any information that can change every minute or even every second.
- Process-as-a-Service: It is a remote resource that can link multiple resources (such as services or data contained within one Cloud or other available “clouds”) to create a single business process.
- Application-as-a-Service: Still, be called Software-as-a-Service. Positioned as “on-demand software” deployed on remote servers, every user can access it via the Internet, with all upgrades and licenses regulated by the service provider. Payment, in this case, is made for the actual use of the latter. Examples include Google Docs, Google Calendar,, online software.
- Platform-as-a-Service (“platform as a service”) The user is provided with a computer platform with an installed operating system and software.
- Integration-as-a-Service: It is an opportunity to receive a complete integration package from the Cloud, including software interfaces between applications and managing their algorithms. This includes the enterprise application’s well-known services and functions (EAI)centralization, optimization, and integration packages but provided as a cloud-based service.
- Security-as-a-Service: It provides users the ability to quickly deploy products that allow for the safe use of web technologies, e-mail, and local networks, allowing users of this service to save on deployment and maintain their security system.
- Management/Governance-as-a-Service (“administration and management as a service”) allows you to manage and set the parameters of one or many “cloud” services. These are main parameters such as topology, resource use, virtualization.
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (“infrastructure as a service”) The user is provided with computer infrastructure, usually virtual platforms (computers) connected to the network, which he independently adjusts for his purposes.
- Testing-as-a-Service (“testing as a service”) allows testing of local or “cloud” systems using test software from the “cloud” (no hardware or support in the enterprise is required).
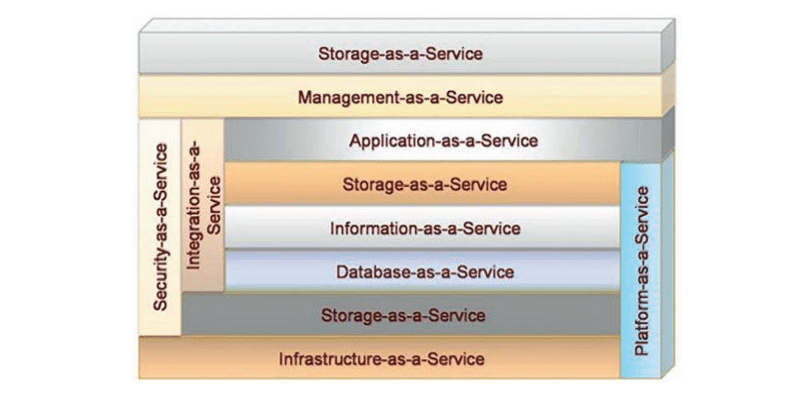
For clarity, let’s summarize all these services of the “cloud” architecture, in one scheme behind which are cloud technologies.
Now let’s look at what cloud technologies are in the form of ownership. Here, highlight three of their categories:
- Public
- Private
- Hybrid
Briefly on each:
- The public Cloud is an IT infrastructure used by multiple companies and services at the same time. Users cannot manage and maintain this “cloud,” and all responsibility for these matters rests with the owner of the resource. Any company and an individual user can become a subscriber of the services offered. Examples include online services such as Amazon EC2, Google Apps/Docs, Microsoft Office Web.
- A private cloud is a secure IT infrastructure controlled and operated for the benefit of a single organization. The organization can manage the private “cloud” on its own or entrust the task to an external contractor. Infrastructure can be placed either in the customer’s premises or at the external operator (or partly from the customer and partly at the operator).
- A hybrid cloud is an IT infrastructure that uses the best public and private Cloud to solve a problem. This type is often used when an organization has seasonal activity periods; in other words, once the internal IT infrastructure fails to meet current tasks, some of the capacity is transferred to a public “cloud” (e.g., large amounts of statistical information) and to provide users with access to enterprise resources through a public “cloud.”
Entangled? Nothing, soon we will analyze the examples, and everything will fall into place 😉
Cloud Computing Opportunities
Now let’s look at the possibilities of cloud computing:
- Access to personal information from any computer connected to the Internet
- You can work with information from different devices (PC, tablets, phones, etc.)
- No matter what operating system you prefer to work in, web services work in any OS browser.
- The same information, both you and others, can be viewed and edited simultaneously from different devices.
- Many paid programs have become free (or cheaper) web apps.
- If something happens to your device (PC, tablet, phone), you won’t lose important information because it is no longer stored in the devices’ memory.
- New and updated information is always on hand.
- You always use the latest version of the software and do not have to watch updates.
- You can combine your information with other users.
- It is easy to share information with loved ones or with people from anywhere in the world.
Opportunities, however, have their drawbacks (where without them), which should also be mentioned.
“A spoonful of tar” – drawbacks:
- The need for a permanent connection.
- To access cloud services, you need a permanent internet connection.
- The software and its “customization.”
- There are limitations to the software that can be deployed on the “clouds” and provide to the user. The user has limitations in the security used and sometimes cannot customize it for their purposes.
- The confidentiality of the data stored in public “clouds” is currently controversial. In most cases, experts agree that it is not recommended to store the most valuable documents for the company on the public “cloud” because there is currently no technology that would guarantee 100% data privacy.
- The Cloud itself is a reasonably reliable system, but the attacker gains access to a vast data store once it penetrates. Another drawback is the use of virtualization systems in which, as a hypervisor, the cores of standard OS (e.g., Windows)are used, allowing the use of viruses and system vulnerabilities.
- Expensive equipment.
- To build your Cloud, you need to allocate significant material resources, which is not beneficial to newly created and small companies.
- Further monetization of the resource.
- Companies in the future may decide to charge users for the services provided.
As you can see, there are two sides to the coin. However, the development of technology does not harm and may even spur.
Cloud technology is a user’s view. Solution review
We came to perhaps the most interesting (and so beloved by many readers) part of the article – examples and practice. Here we will look at what solutions, services, programs already exist on the market and what is worth paying attention to. Let’s start with services:
- Apple’s iCloud Cloud Service (replaced by MobileMe), fully automatic and free (albeit with few functional limitations). It saves all sorts of content (mail, calendar, contacts, documents, music, videos and images, etc.) on servers. It then delivers it to all devices(iPhone, iPad, iPod touch, Mac, and PC)using wireless Push technology.
- Google Play: It is a new cloud service called Google Play from the “Corporation of Goodness,” designed to host users of movies, music, apps, and books on servers specifically designed to store digital information. Access to the service is provided directly from the browser, regardless of the OS, and therefore can be carried out from both PC and mobile devices based on Android. Each user has the opportunity to place and store up to 20,000music records on a complimentary basis, as well as directly download to the server purchased in stores(Android Market, Google Music, and Google eBookstore) digital goods – movies, e-books, programs, music tracks, both bought and rented.
- OnLive: I think that everyone is friendly service, I have already written about it. Provides the ability to play modern games even on the most straightforward and weakest computer. Technically, this is as follows: the game itself is located on a remote server, and there is also processing graphics, which comes to the computer to the user already in the “ready” form. Those calculations that a graphics card, processor, etc., perform when you play a regular game on your computer are already done on the server. Your computer is only used as a monitor that receives the final picture. If you don’t understand, all this means that all computer performance problems and the amount of space on the hard drive are automatically removed because you don’t even need installation. Also, there is no need to pay quite a lot of money immediately for the product (game, etc.), which you do not necessarily have to like. To the fact that it is no secret that most games do not want to go through again, so it turns out that the cost of a few hours (or even a few days) of pleasure – unnecessarily high. Where would be a more convenient option, in which you would pay only for the time you play. Or – you would pay a small fixed amount monthly, which would allow you to play without restrictions in any of the available games.
- Xbox Live: It is another well-known gaming service that provides rich Internet functionality and is related to cloud technology. The essence of the service is that the owners of Xbox 360 and PDA based on Windows Phone 7 can play with each other in computer games and communicate and buy add-ons and various multimedia content in the online store. It turns out that the service creates a virtual universe for gamers, the components of which are located not on the consoles of end-users but in the Cloud.
Thus, the last two services offer games as a service. Now let’s imagine that we are not talking about games but software. You do not pay for the product per se (for the box with the disk) but for the specific functions/opportunities that it provides you. Interesting? That’s what I :).
A small note
And since we, as users, are most interested in software (rather than all platforms there, as a service), now we will consider the “software landscape”(SaaS)of the clouds. In other words, let’s give the most popular software solutions, which, within the concept of cloud technology, in fact, now exist in the market.
Actually, according to SaaS-concept, as mentioned above, you pay not a lump sum, buying a product, but as if to rent it. Moreover, use precisely the functions you need (and pay for them the same) accordingly. For example, once a year, you need a particular program, and more often you use it, you are not going to. So why buy a product that will lie idle?
And why spend a place on it (in the apartment, if it’s a box with a disk, or on a Winchester if it’s a file)? That’s right, not why, because there is an alternative – a free online service (providing this program’s full functionality).
Dealing with documents in cloud technology
This is the path that two headliners of the IT industry (and part-time competitors) – Google and Microsoft– went along the way. Both companies have released sets of services that allow them to work with documents.

On the part of Google – it’s their Google Docs (now Google Drive):
Free online office includes a word, table processor, and “snaps” to create presentations and an internet service cloud storage of files with file-sharing functions.
It is a web-oriented software, a program that works within a web browser without installation on the user’s computer, i.e., a kind of alternative version of all word, Excel, , etc., without the need to buy and all that. Documents and tables created by the user are stored on a particular Google server or exported to the file.
This is one of the program’s key advantages, as access to the entered data can be made from any computer connected to the Internet (with access protected by a password).
Microsoft’s Microsoft is their Microsoft Office Web Apps:
Microsoft Office Web Apps allow you to take advantage of Microsoft Office’scapabilities through a web browser and work with documents (not only to view them but also to edit them) directly on the website where they are stored.
Thus, the documents look in the browser just like in Office programs, i.e., complete, so to speak, unification.
It’s also worth noting that both services are closely related to mail(Gmail in the first case and Hotmail in the second) and file storage. To use Google Docs, it is enough to start a free Google account, and you will get a set of programs to work with texts, spreadsheets, etc., right in the browser. For many, Google Docs has wholly replaced, as mentioned above, the paid MS Office.
If we sum up (on these two services), we can say that the user is transferred from his usual offline environment to online.
Let’s move on.
Cloud technology and data storage
- Dropbox: You may have multiple computers, but you can share a file folder for all your PCs and even your smartphones with this cloud storage. The most exciting thing is that there is no need to do any particular actions because the operating system will perceive the shared folder, like all other folders on Winchester. A dropbox will take care of synchronization. The work allows you to store up to 2GB of data for free. The main focus of it is on synchronization and information exchange. Dropbox has a download history so that after deleting files from the server, you can recover the data, plus the file change story that is available for the last 30
- Windows Live SkyDrive: SkyDrive allows you to save up to 7GB (and you can share up to 100MB of files) with information in a standard folder-ordered form. Images have a preview mode, as well as the ability to show them as slides. In addition to being integrated with Microsoft Office, the service also supports the new Windows 8 operating system (or rather, the SkyDrive client is built into Metro applications and allows you to upload documents and photos to the Cloud in one click, open files from a small store).
- And of course, Google Drive. There will be a separate article about it.
By the way, not only all offices and file storage use cloud technologies. For example, in the digital “evil” camp, they also relied on cloud computing. And here’s the result – free antivirus Panda Cloud Antivirus.
It is based on innovative “collective intelligence” technology (which automatically detects new threats in a minimal amount of time). It minimizes the impact of protection on your computer’s system resources by leveraging cloud technology’s computing power for most operations: analyzing, blocking, and trying to remove malware.
The antivirus servers use information from millions of Panda antivirus users worldwide to automatically detect and classify new types of malware that appear every day.
In a nutshell, somehow so, although there are still a lot of services that could be told, but then have to write a volume of War and Peace 🙂 So let’s get to the end of the day.
Cloud, Cloudy or clear?
Simply put, the Cloud is an opportunity always to have guaranteed and secure access to all your personal information, as well as avoiding the need to keep in your pocket a lot of extra things (all kinds of flash drives, drives, wires, and all that) or to buy a new computer/components/programs/games, etc.
Of course, it is still difficult for the average user to fully appreciate (and reveal) their full potential, but it is visible to the naked eye.
Thus, without a doubt, cloud technology’s future seems very rosy because such giants(Microsoft, Apple, and Google) just so certainly do nothing. It is pretty clear that if they came into this uncharted territory, they are not going to leave it because two years ago, the concept of “cloud” seemed only a beautiful idea and a bold experiment.
Today the benefits of cloud technologies can feel even those people who are not associated with software development, web technologies, and other highly specialized things (the Xbox as mentioned above Live, Live Windows, OnLive, Google Docs).






